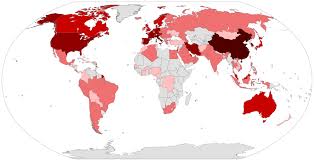
The 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic is an ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The outbreak was first identified in Wuhan, Hubei, China, in December 2019 and recognised as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 11 March 2020. As of 17 March, more than 188,000 cases of the disease have been reported in over 160 countries and territories, resulting in more than 7,500 deaths and around 80,000 recoveries. Regions affected by major outbreaks include mainland China, Europe, Iran, South Korea, and the United States. On 13 March, the WHO stated that Europe had become the new epicentre of the pandemic.
The virus is transmitted primarily between people in a similar manner to influenza, via respiratory droplets from coughing, sneezing or exhalation including speaking. It is considered to be most contagious when those infected appear symptomatic, although transmission is still possible if those infected appear asymptomatic. The time between exposure and symptom onset is typically five days, but may range from two to fourteen days. Common symptoms include fever, cough and shortness of breath. Complications may include pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Currently, there is no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment; treatment efforts consist of symptom alleviation and supportive therapy. Recommended preventive measures include handwashing, covering the mouth when coughing, maintaining distance from other people (particularly those who are unwell), and monitoring and self-isolation for fourteen days for people who suspect they are infected